Introduction: Understanding the Importance of Quality Magnesium Sulfate
Magnesium Sulfate (MgSO4) is a vital inorganic compound with a wide range of applications across the medical, agricultural, and industrial sectors. From its role as a critical nutrient in fertilizers to its use as a tanning aid in leather processing, the quality of Magnesium Sulfate directly impacts the effectiveness and safety of the end product.
For B2B buyers, sourcing this compound is not just a matter of procurement; it is a critical decision that affects operational efficiency, regulatory compliance, and final product integrity. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of how quality Magnesium Sulfate is produced, the key metrics that define its grade, and how buyers can effectively vet suppliers to ensure a consistent, high-purity supply.

1. What is Magnesium Sulfate? An Overview
Definition and Composition:
Magnesium Sulfate is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula MgSO4. While it exists in various hydration states (such as Heptahydrate and Monohydrate), its quality is universally determined by its purity and the presence of controlled impurities.
Key Characteristics:
Specific Particle Size: The particle size (granulometry) of the final product is carefully controlled to ensure proper solubility and reactivity.
High Purity: Reputable manufacturers ensure that product purity is consistently maintained above 99%, which is a critical indicator of quality for sensitive applications.
Controlled Impurities: Rigorous quality control processes limit the levels of impurities. This is strictly monitored for heavy metals like lead (Pb) and arsenic (As), particularly for medical-grade products where patient safety is paramount.
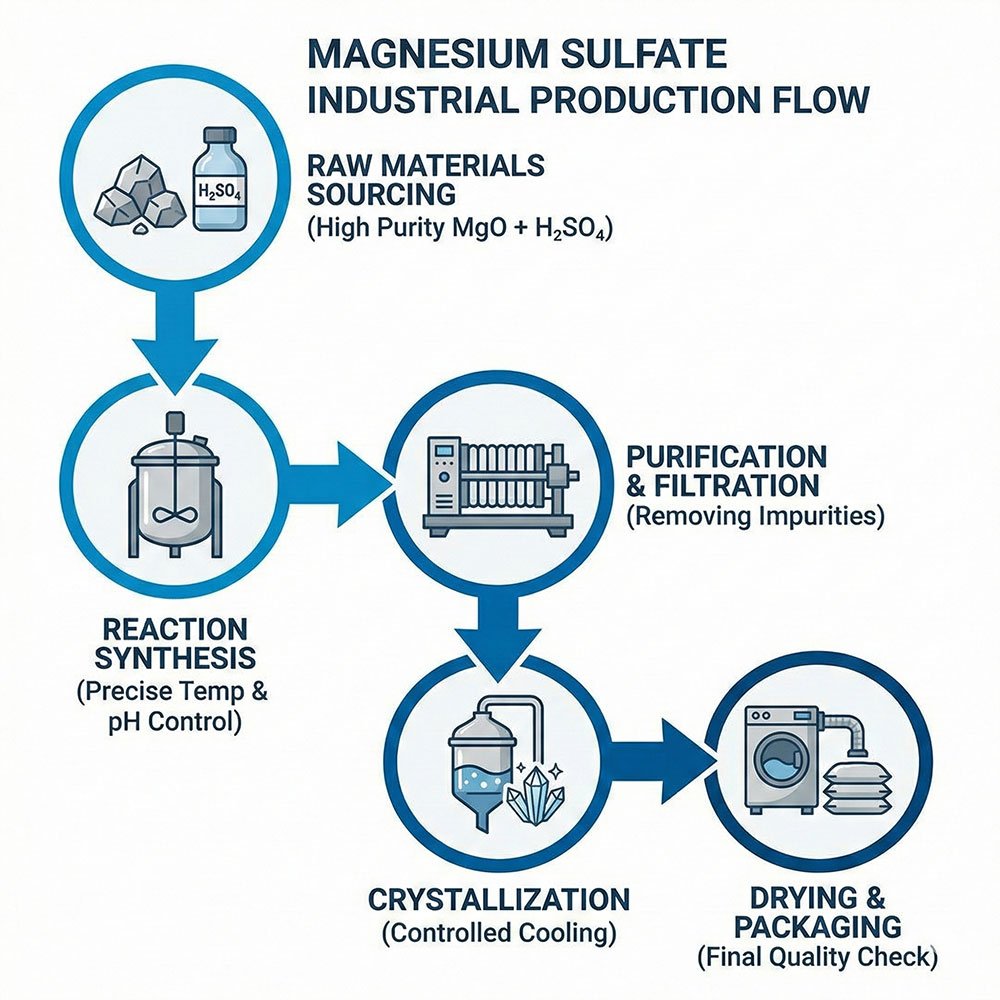
2. The Manufacturing Process: From Raw Materials to Final Product
Understanding the production process offers insight into a manufacturer’s technical capabilities and commitment to quality.
Sourcing High-Grade Raw Materials
The manufacturing process begins with the careful selection of high-purity raw materials. The primary components are a magnesium source (such as Magnesium Oxide or Magnesium Carbonate) and Sulfuric Acid.
Purity Thresholds: Quality-focused manufacturers ensure the purity of the magnesium source is not below 98%.
Source Selection: Leading suppliers often prefer Magnesium Oxide derived from natural magnesite. This source inherently contains lower levels of heavy metals compared to synthetic alternatives, preventing contamination from the very start of the process.
Key Production Stages
The transformation from raw materials to a finished product involves several precisely controlled stages:
- Reaction Synthesis: The magnesium source and sulfuric acid are mixed in a reaction vessel. Process parameters such as temperature and pH are carefully controlled to ensure a complete and efficient chemical reaction.
- Purification and Filtration: The resulting Magnesium Sulfate solution is filtered, often through multi-stage systems, to remove insoluble impurities and any unreacted raw materials.
- Crystallization: The purified solution is concentrated and then cooled or subjected to evaporation. This process allows magnesium sulfate crystals to form.
- Note: This step is critical; improper temperature control can significantly impact crystal structure and product purity.
- Separation and Drying: The crystals are separated from the remaining liquid using a centrifuge. The remaining liquid (‘mother liquor’) is often recycled to minimize waste. The crystals are then dried, typically in a fluidized bed dryer, to achieve the specific moisture content required for MgSO4·7H2O or MgSO4·H2O.
- Screening and Packaging: Finally, the dried product is screened to classify it by particle size and packaged in sealed, moisture-proof bags to prevent caking.
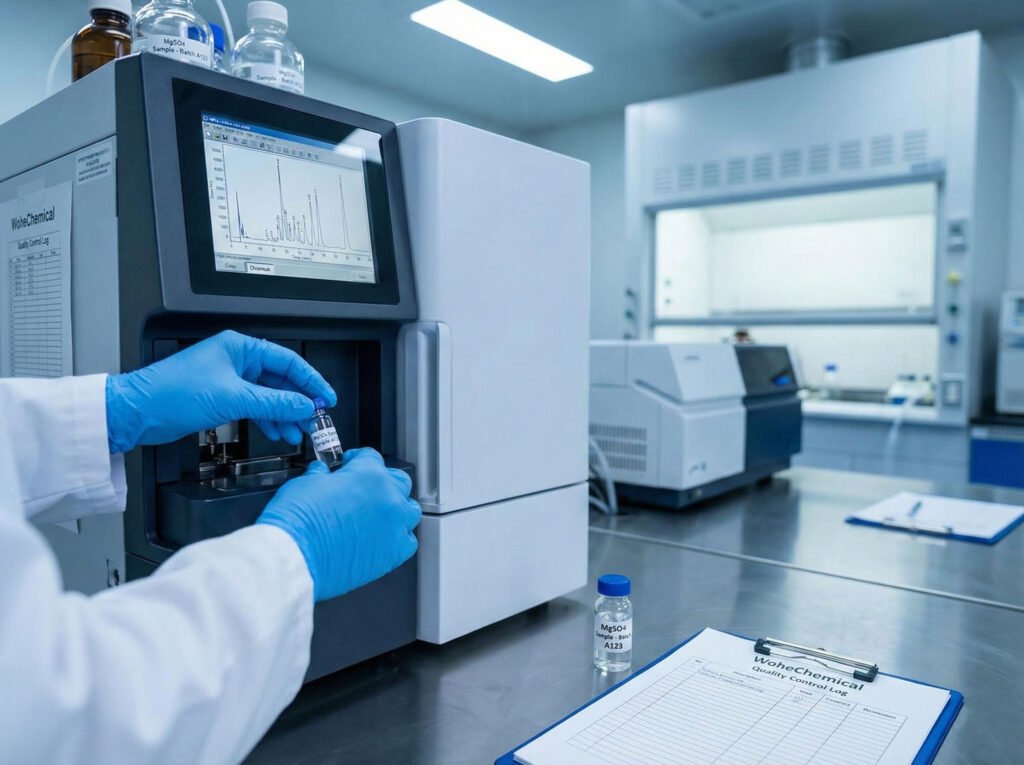

3. Critical Quality Control Points
The final quality of Magnesium Sulfate is determined by several critical factors throughout the manufacturing process.
Precision Process Control
Precise control over process parameters is vital to guarantee high purity. Leading manufacturers use automated systems to continuously monitor:
- Reaction Temperature: Typically maintained between 60-80°C.
- pH Level: Strictly kept between 5-6.
Maintaining these parameters prevents the decomposition of the product and ensures consistent batch-to-batch quality.
Adherence to International Standards
Compliance with national and international standards is non-negotiable. For export products, manufacturers must comply with regulations such as the European Union’s REACH or US FDA standards.
Impurity Limits by Grade:
| Grade | Key Specification |
| Medical Grade | Lead (Pb) Content: ≤ 5mg/kg |
| Medical Grade | Arsenic (As) Content: ≤ 2mg/kg |
| Industrial Grade | Focus on >99% purity and specific particle size distribution suitable for manufacturing. |

4. A Buyer’s Checklist: How to Choose a Reliable Supplier
Use this checklist to assess the capabilities and reliability of potential Magnesium Sulfate suppliers:
Verify Raw Material Purity: Ask for documentation on the purity of the magnesium source. A supplier using >98% pure inputs is building quality in from the start.
Scrutinize Process Control: Inquire about their use of automated systems for monitoring reaction temperature and pH. This capability indicates a modern, reliable process.
Demand Quality Documentation: Request a Certificate of Analysis (COA) for each batch. This is non-negotiable proof that the product meets specifications for purity and heavy metals.
Confirm Compliance: Verify the supplier’s compliance with standards like REACH, ISO 9001, or FDA regulations to ensure smooth import and usage.
5. Guidelines for Proper Storage and Handling
Proper storage is essential to maintain the free-flowing nature of Magnesium Sulfate.
Product Storage:
- Store in a dry, well-ventilated warehouse.
- Use sealed, moisture-proof packaging (such as PE-lined bags) to prevent the product from absorbing atmospheric moisture, which causes caking.
Safety Precautions:
- Personnel handling the product should wear appropriate Personal Protective Equipment (PPE), including protective gloves, goggles, and respiratory protection, especially when handling fine powder.
- Production facilities must be equipped with essential safety features, including safety showers, eyewash stations, and appropriate fire suppression systems.
6. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: What is the main difference between industrial-grade and medical-grade Magnesium Sulfate?
A1: The primary difference is the much stricter limits on heavy metal impurities in medical-grade products. For example, medical-grade magnesium sulfate must adhere to stringent maximum levels for substances like lead and arsenic to ensure patient safety.
Q2: Why is the production temperature so critical for Magnesium Sulfate quality?
A2: Temperature control during the crystallization stage is crucial. If the temperature is too high, it can cause the magnesium sulfate to decompose, which reduces the final product’s purity. Conversely, if the temperature is too low, the crystallization process slows and can result in fine particles that negatively affect the product’s solubility and handling characteristics.
Q3: What quality documentation should a buyer expect from a supplier?
A3: A buyer should always expect to receive a detailed product testing report or a Certificate of Analysis (COA). This document formally confirms that the product’s purity, impurity levels, and other physical characteristics comply with the agreed-upon specifications and quality standards. This document is your primary tool for batch traceability and quality verification.
Conclusion: Partnering with Quality-Focused Manufacturers
The quality and reliability of magnesium sulfate are not accidental; they are the direct result of a manufacturer’s commitment to rigorous process control. From sourcing high-purity raw materials to executing multi-stage analytical testing, every step in the production chain is critical to the integrity of the final product. By understanding these key quality pillars, B2B buyers can more effectively vet suppliers, mitigate risks, and secure a stable supply of high-purity magnesium sulfate for their specific applications.



